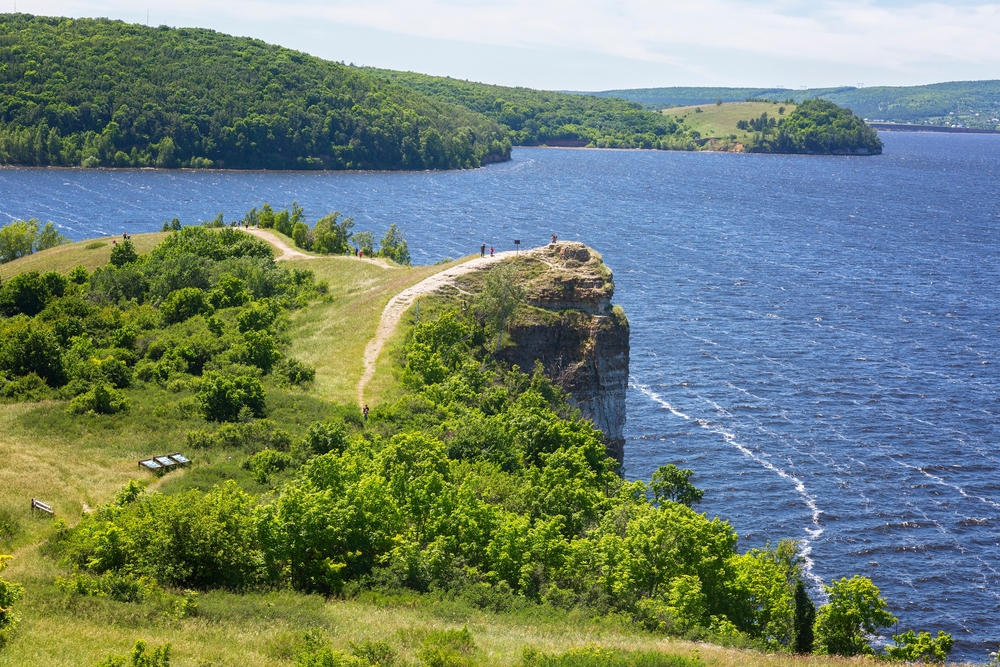Shorsky Overview
Shorsky National Park, known locally as Шорский национальный парк (Shorsky Natsional’nyy Park), is a vast protected area in southwestern Siberia, Russia.
Covering approximately 1,614 square miles (4,180 square kilometers), the park is situated in the Tashtagolsky District of Kemerovo Oblast, about 300 kilometers south of the regional capital, Kemerovo. Established in 1989, Shorsky National Park was created to preserve the unique natural complexes and cultural heritage of the Mountain Shoria region, home to the indigenous Shor people.
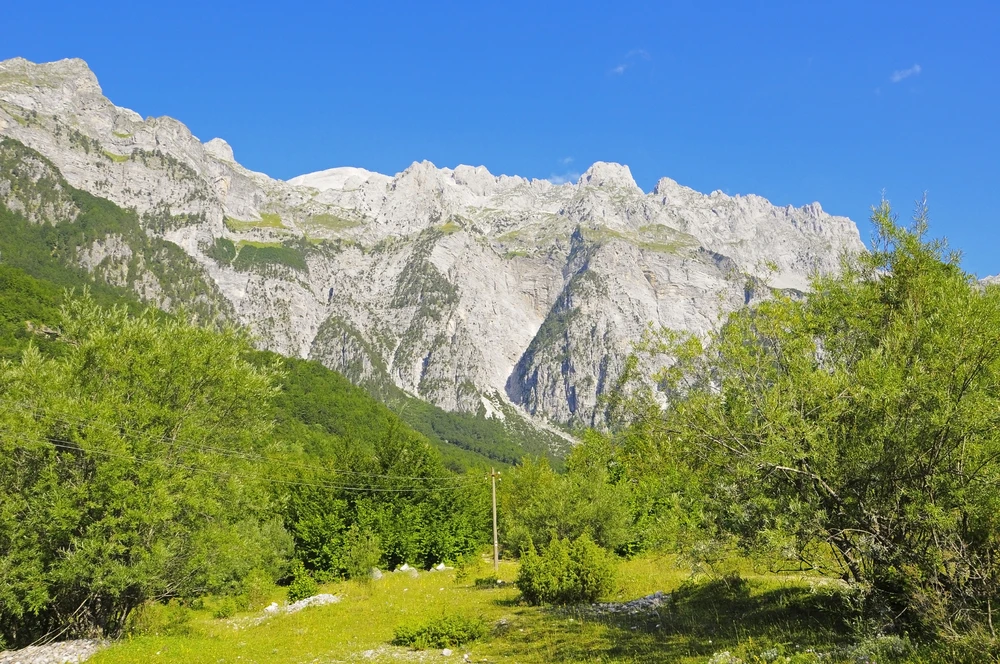
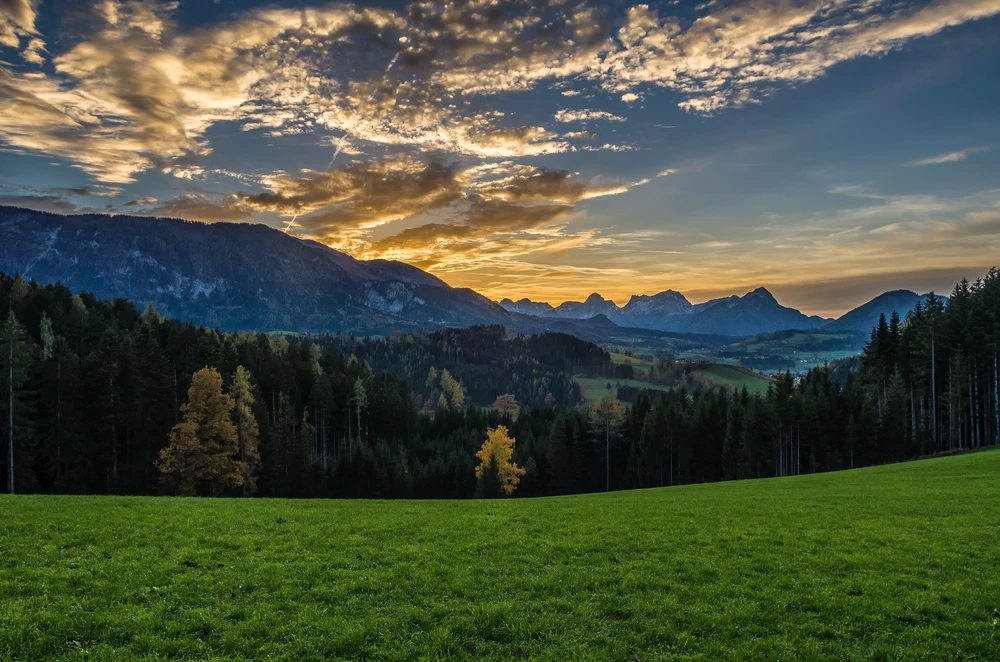
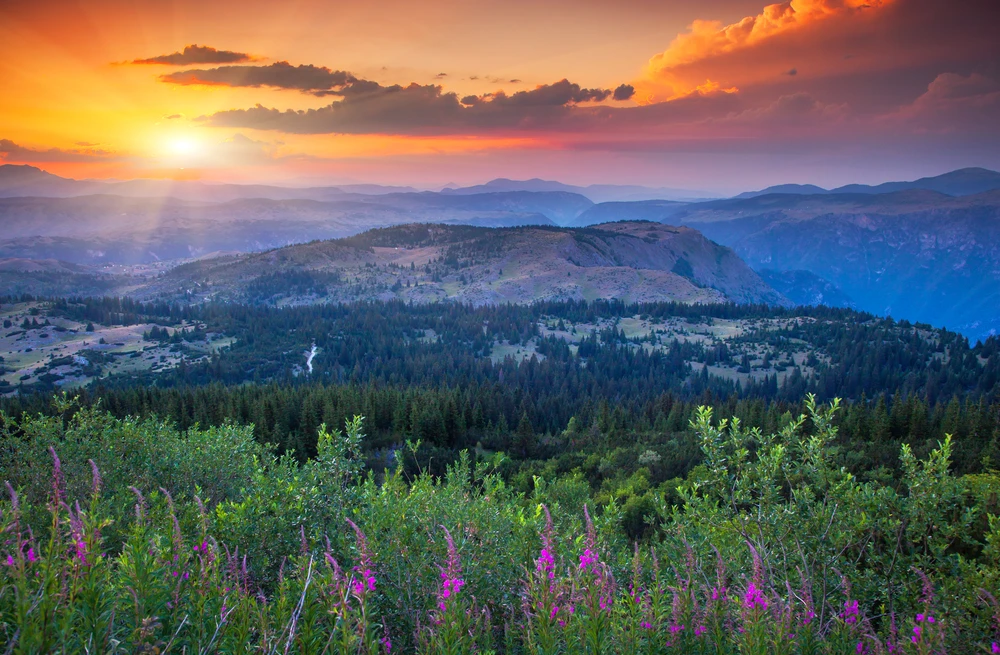
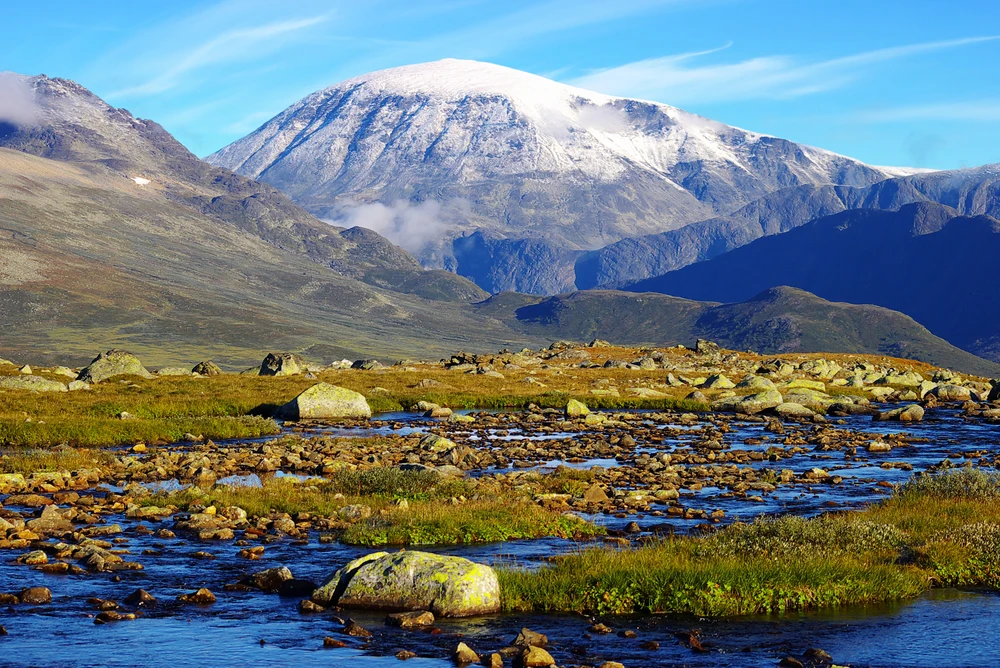
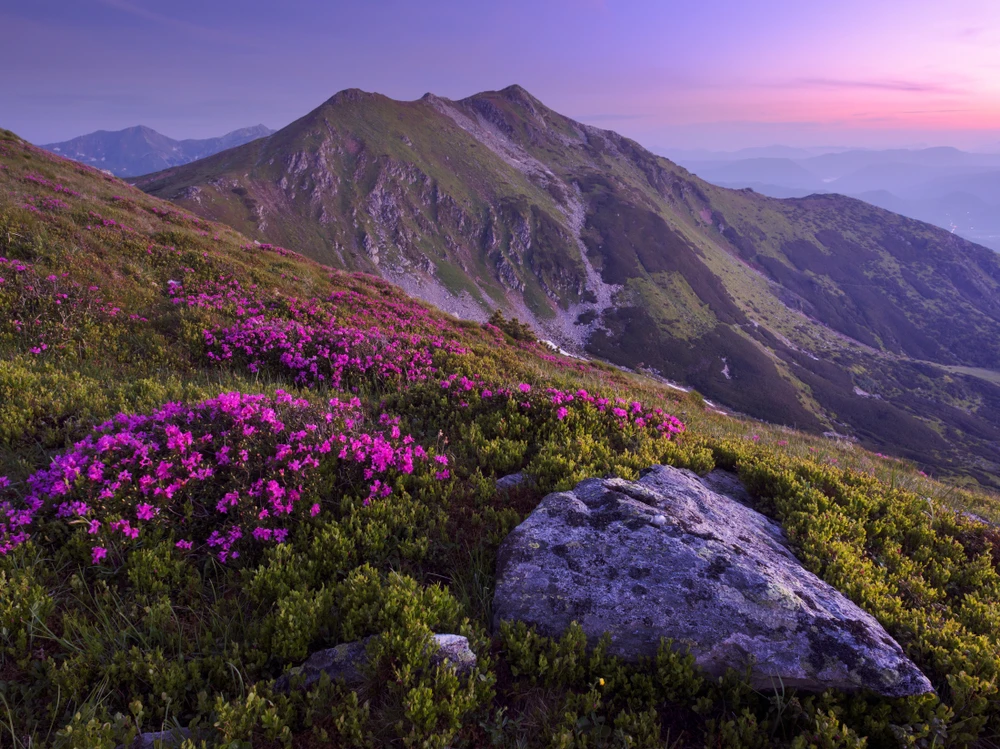
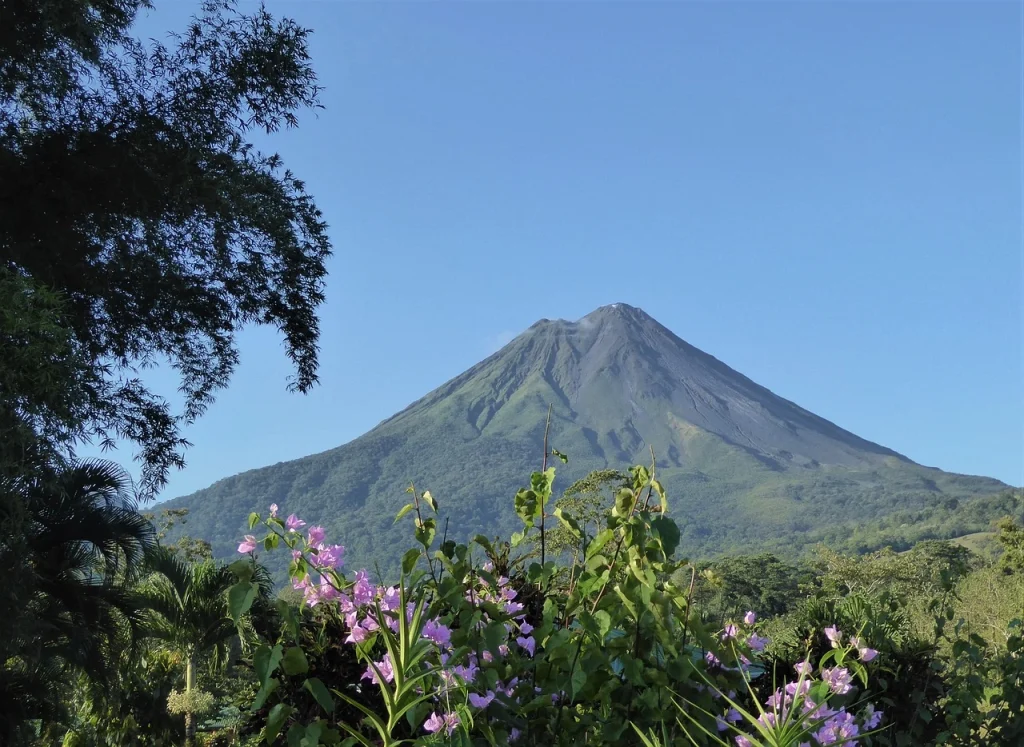
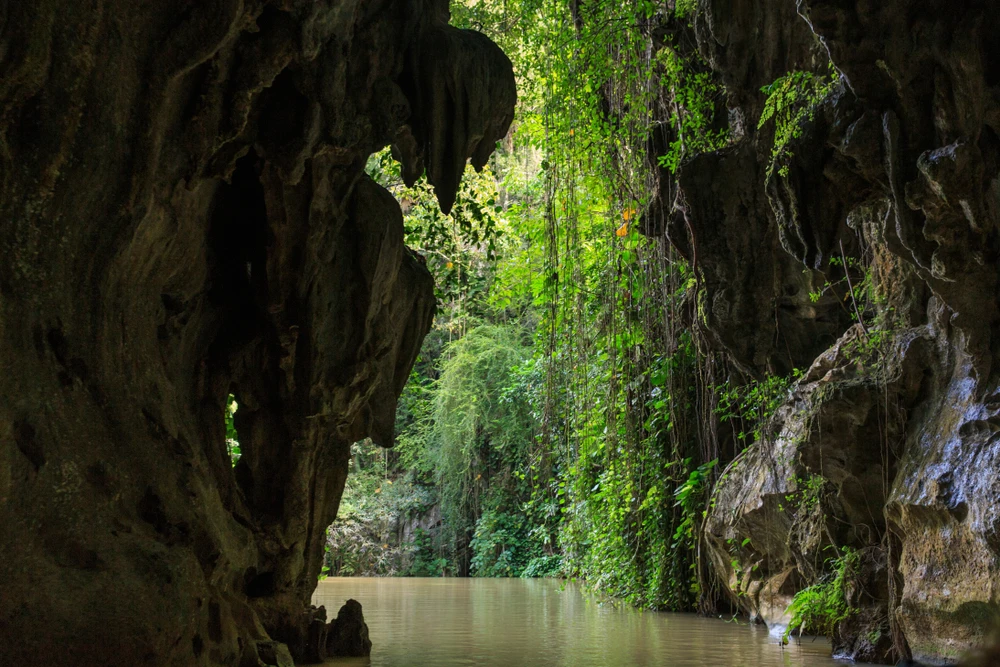
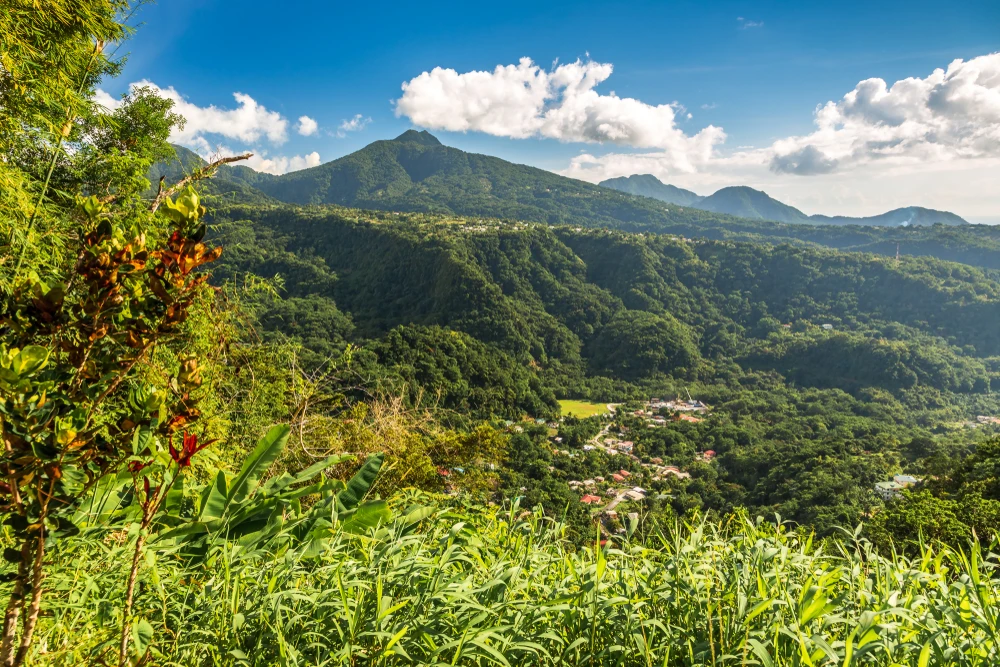
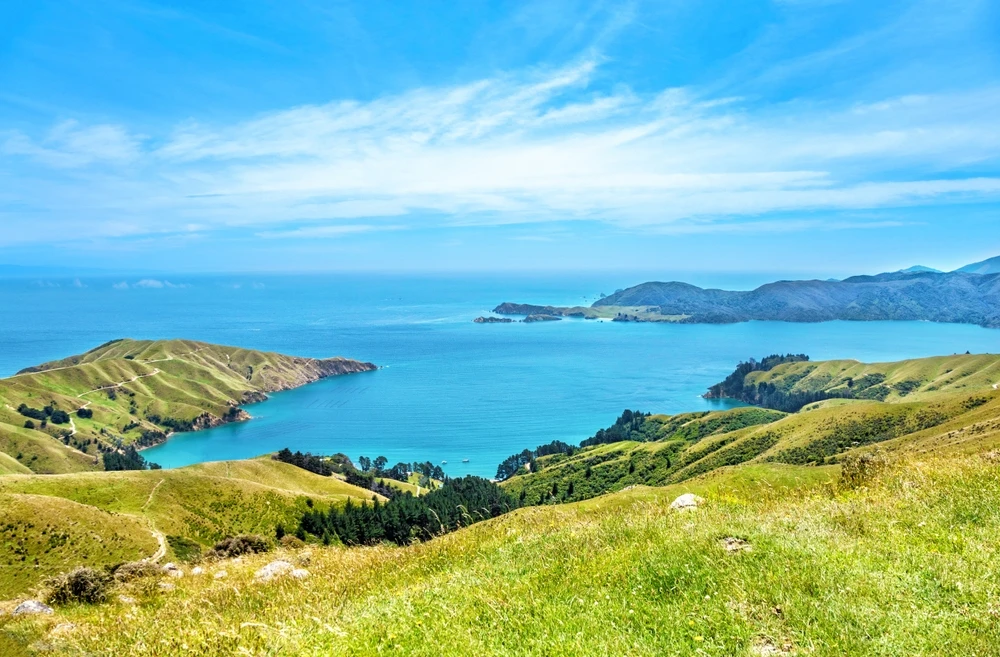
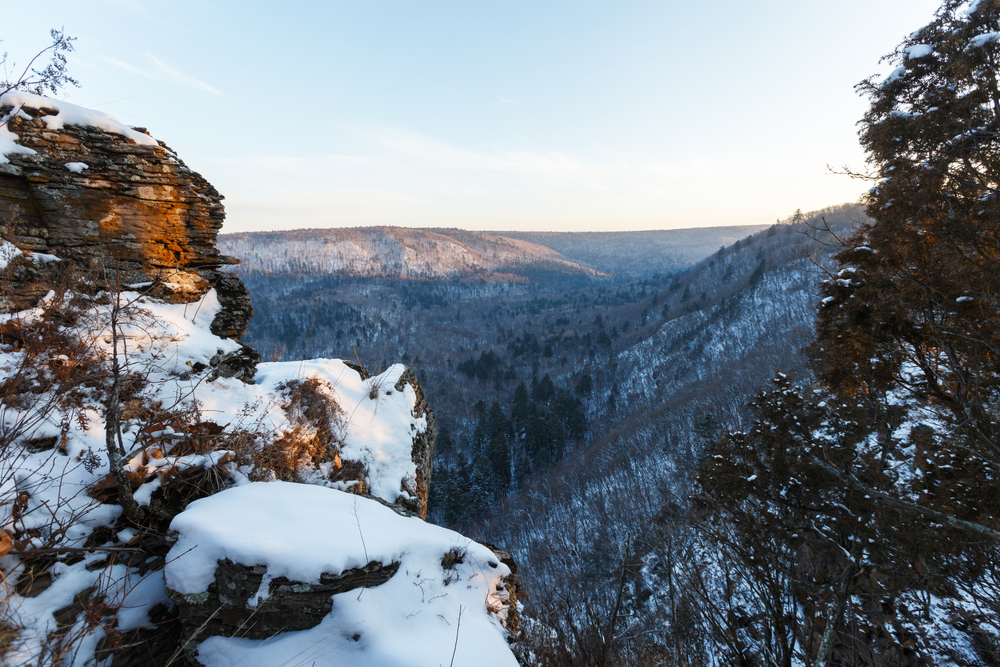
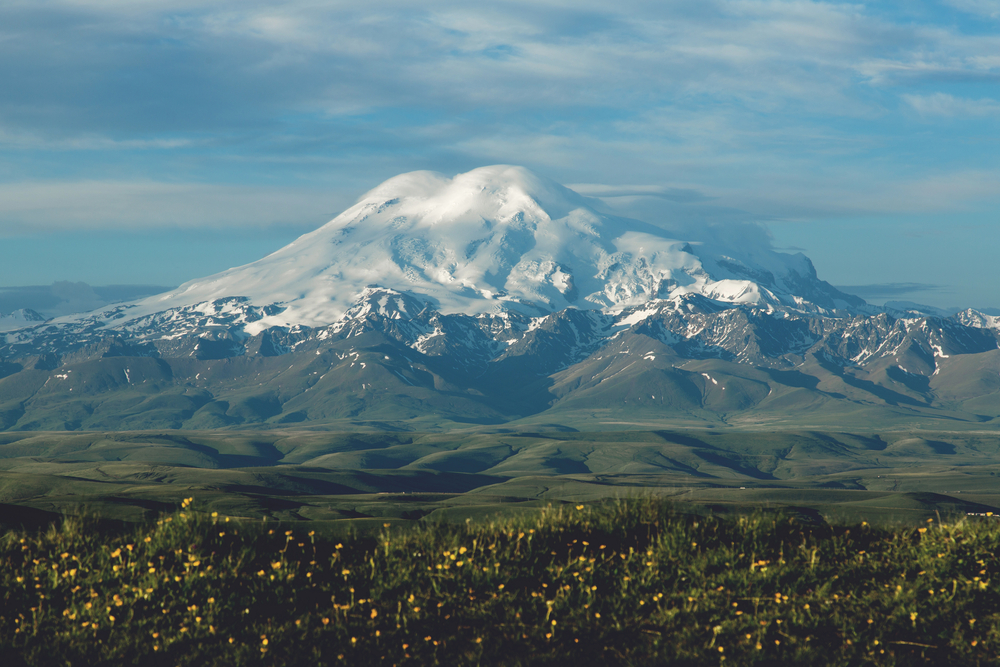
The park’s terrain is predominantly mountainous, with elevations ranging from 500 to 800 meters above sea level, reaching a maximum height of 1,555 meters at Kubez Mountain. This rugged landscape is characterized by deep river valleys, dense taiga forests, and numerous karst formations, including caves and limestone outcrops.
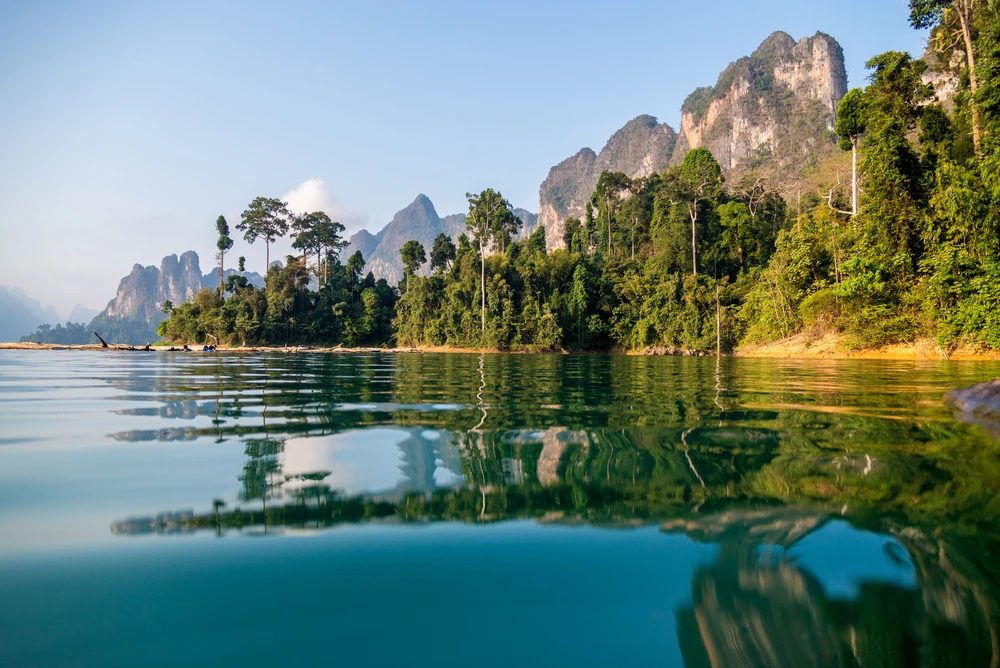
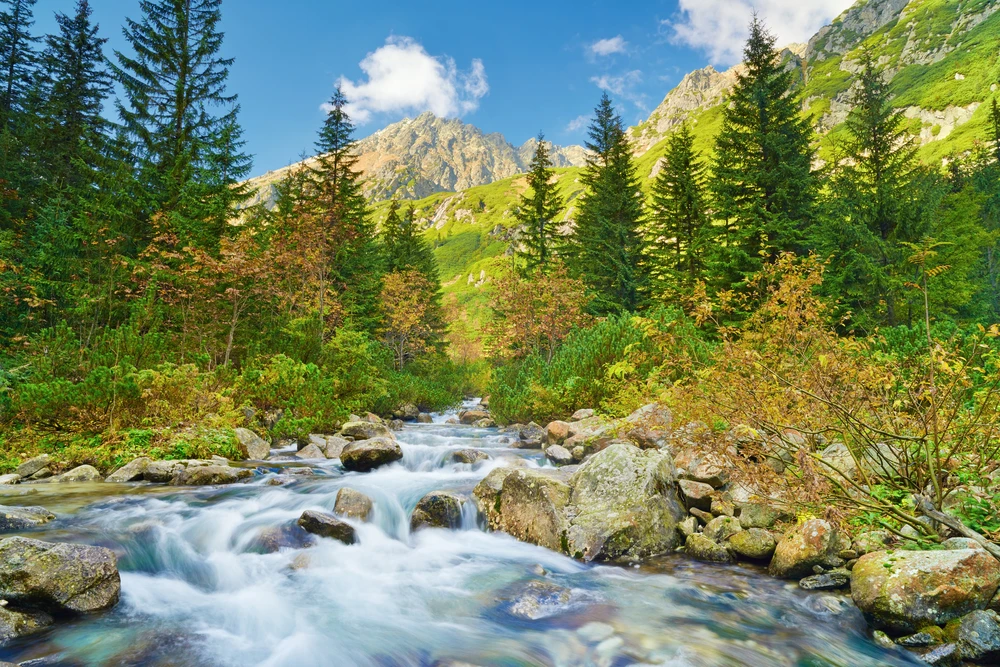
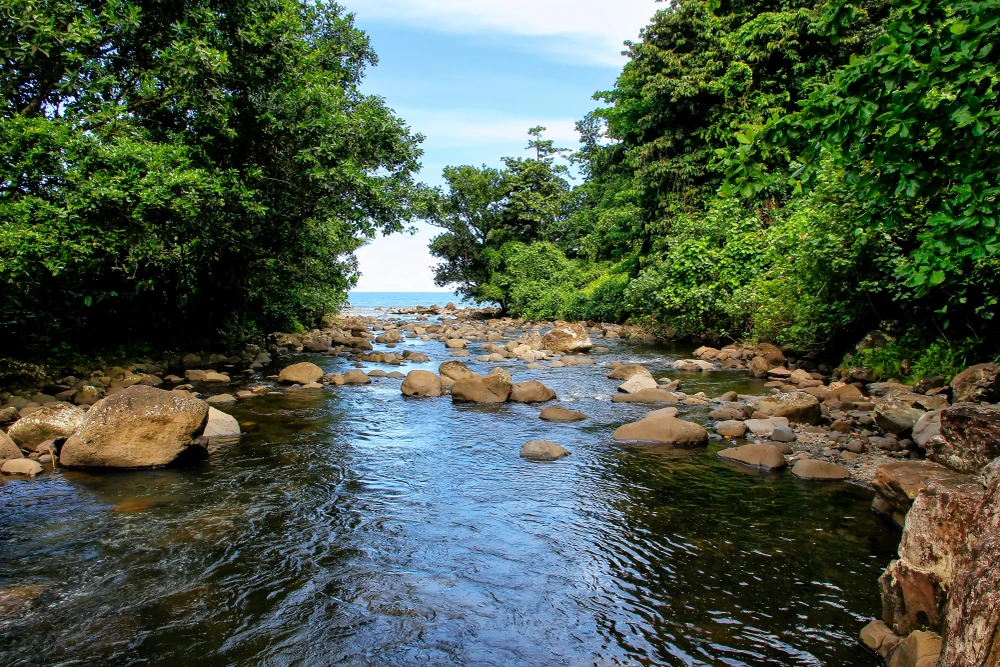
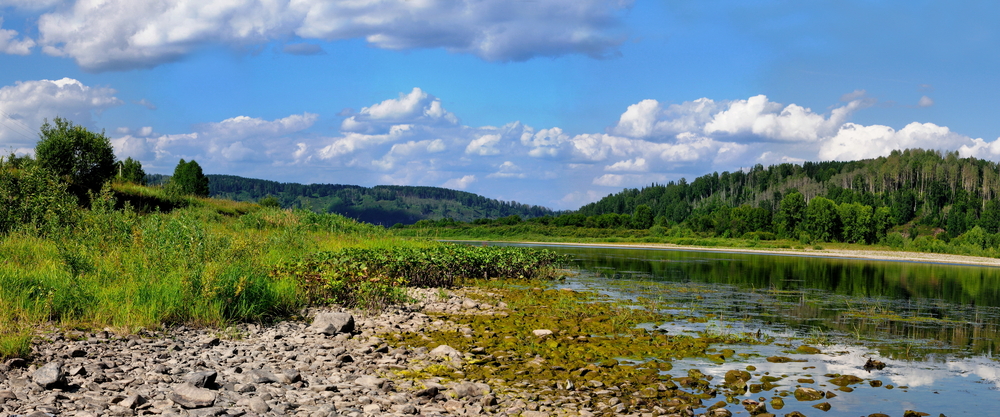
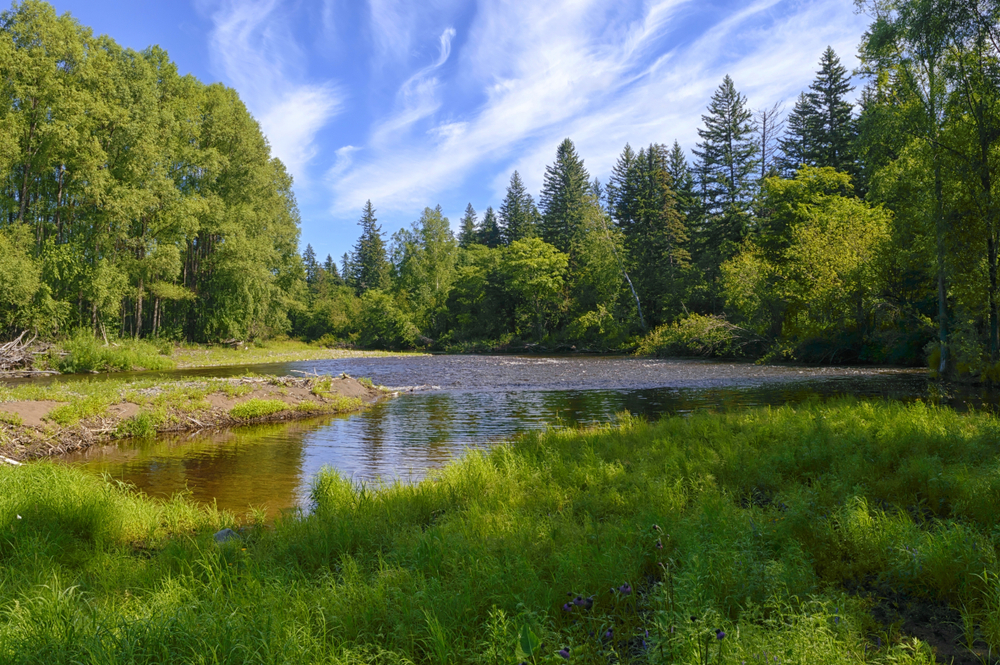
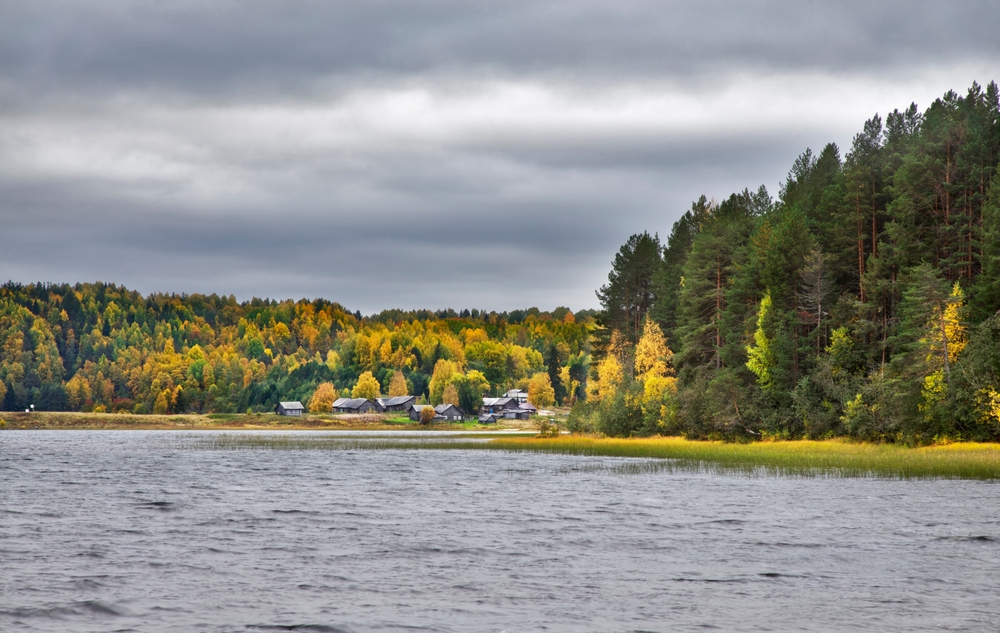
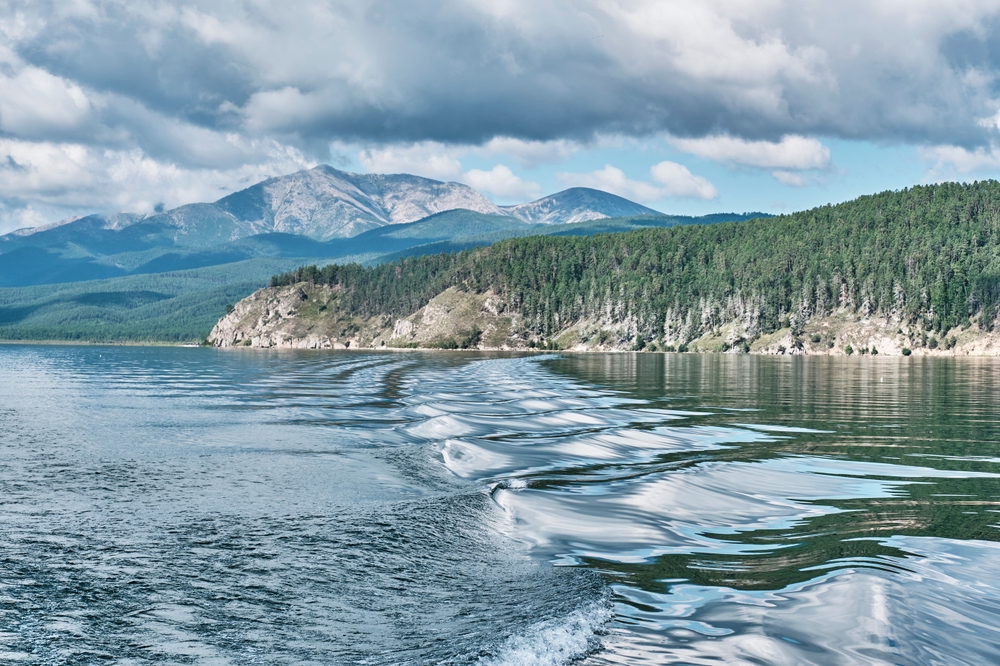
The Mrassu River, meaning “Siberian Pine River” in the Shor language, flows north to south through the park’s center, serving as its main watercourse. The park’s geology, featuring soluble rocks like limestone, has led to the development of springs, caves, and unique rock formations.
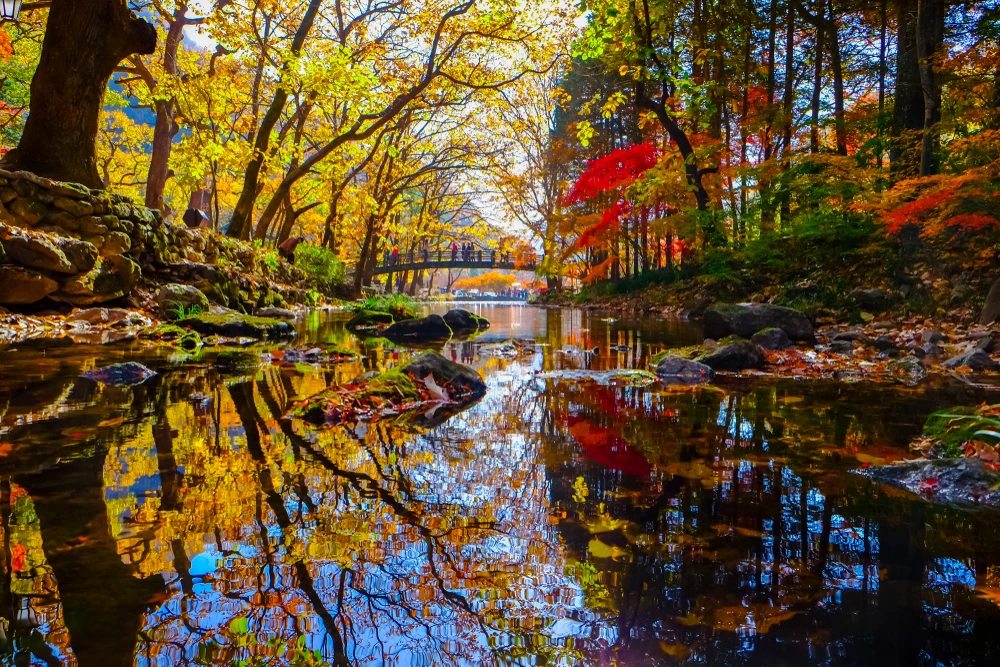
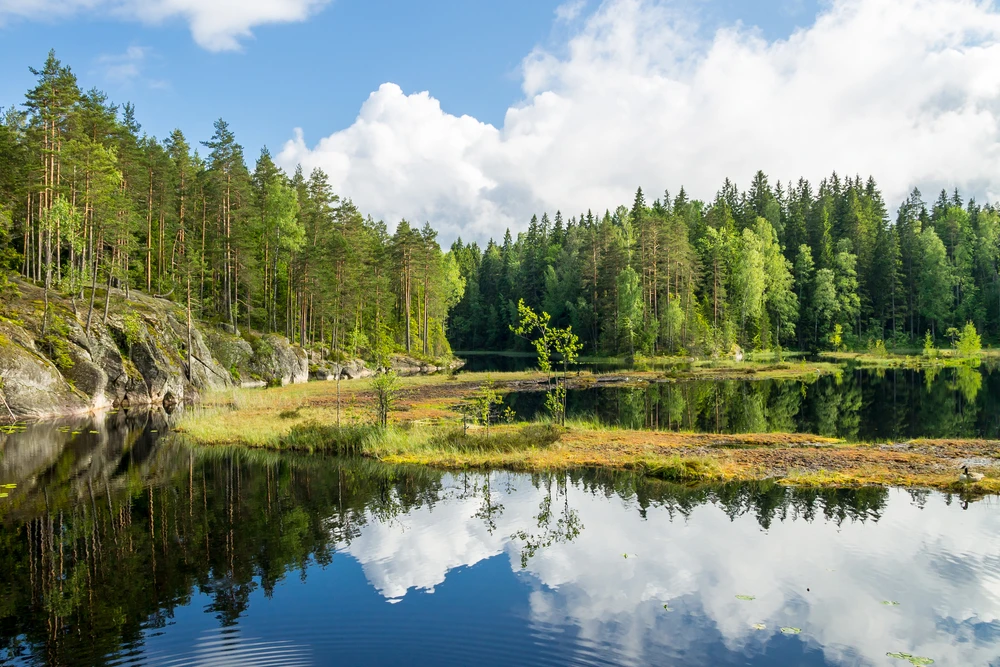
The vegetation in Shorsky National Park is representative of the dark taiga biome, with approximately 92% forest cover. The dominant tree species include Siberian pine and Siberian fir, with occurrences of spruce, pine, and aspen. Willows are commonly found along the floodplains.
The park’s flora is diverse, with records of 51 species of trees and shrubs, over 600 vascular plant species, 300 species of moss, and more than 200 species of mushrooms. This rich biodiversity reflects the park’s position as a transition zone between the Altai Mountains and the West Siberian Plain.
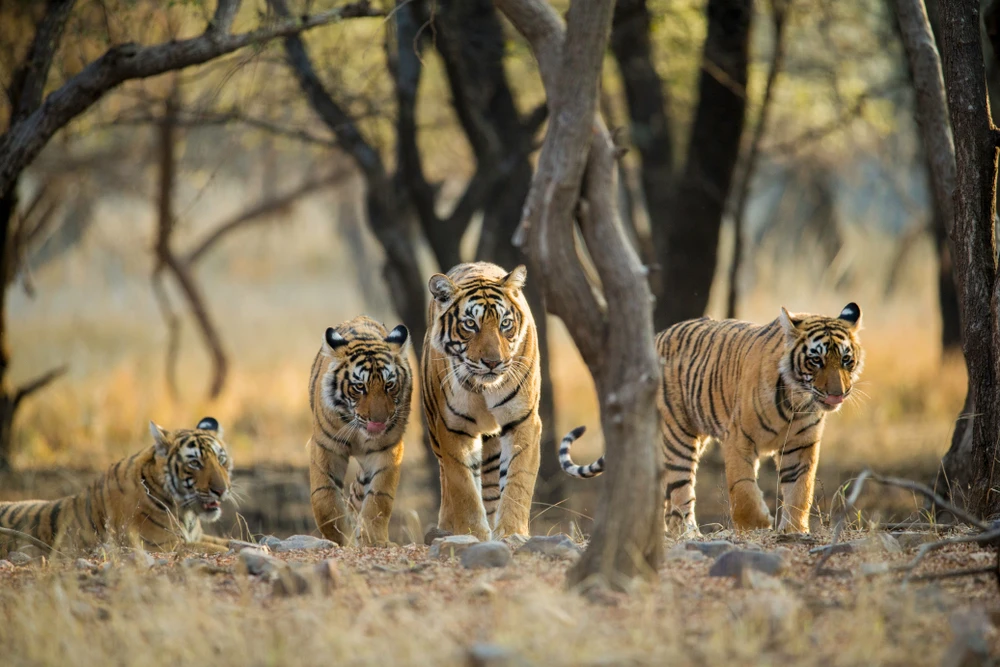
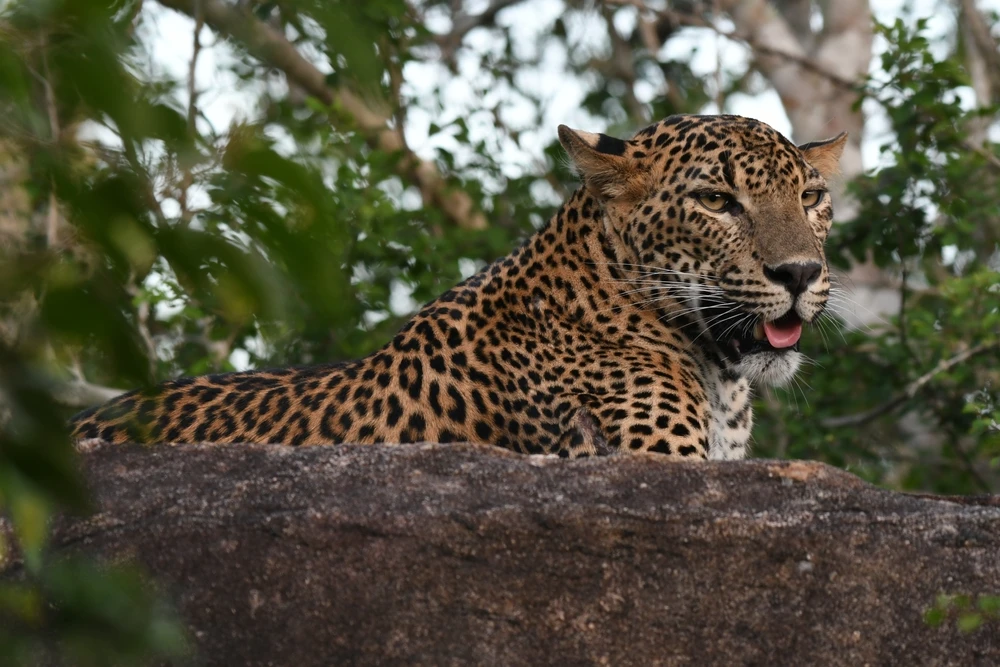
Wildlife in the park is abundant and varied. Large mammals such as brown bears, red deer, roe deer, mink, and sable inhabit the area. The park is particularly known for its sable population.
Other predatory mammals include wolves, foxes, wolverines, weasels, ermines, otters, badgers, and lynxes. Birdlife is equally diverse, with 183 recorded species, offering birdwatchers ample opportunities to observe various avian species in their natural habitats.
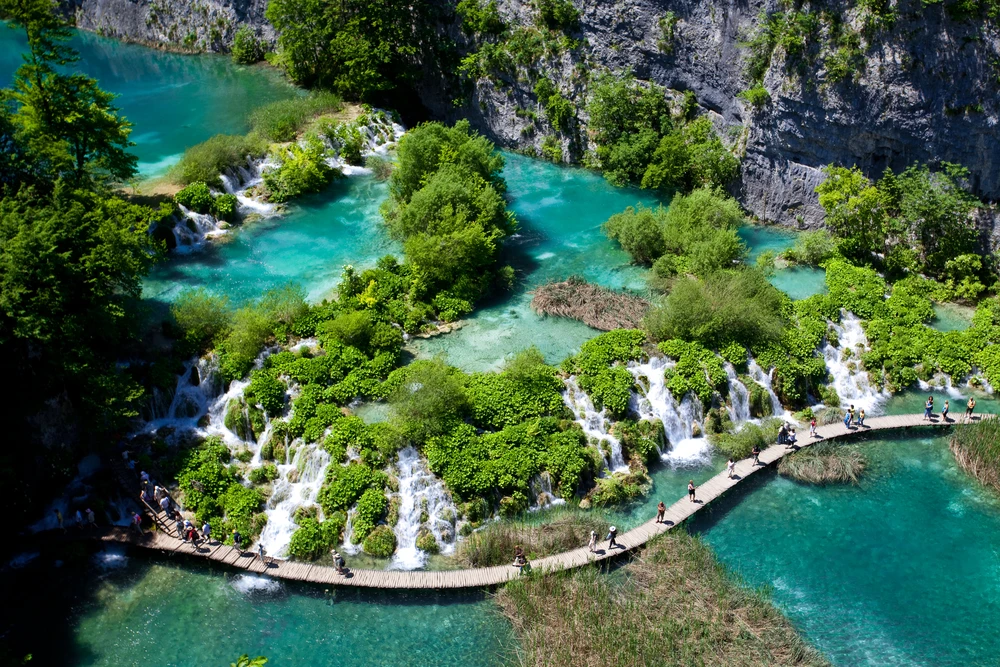
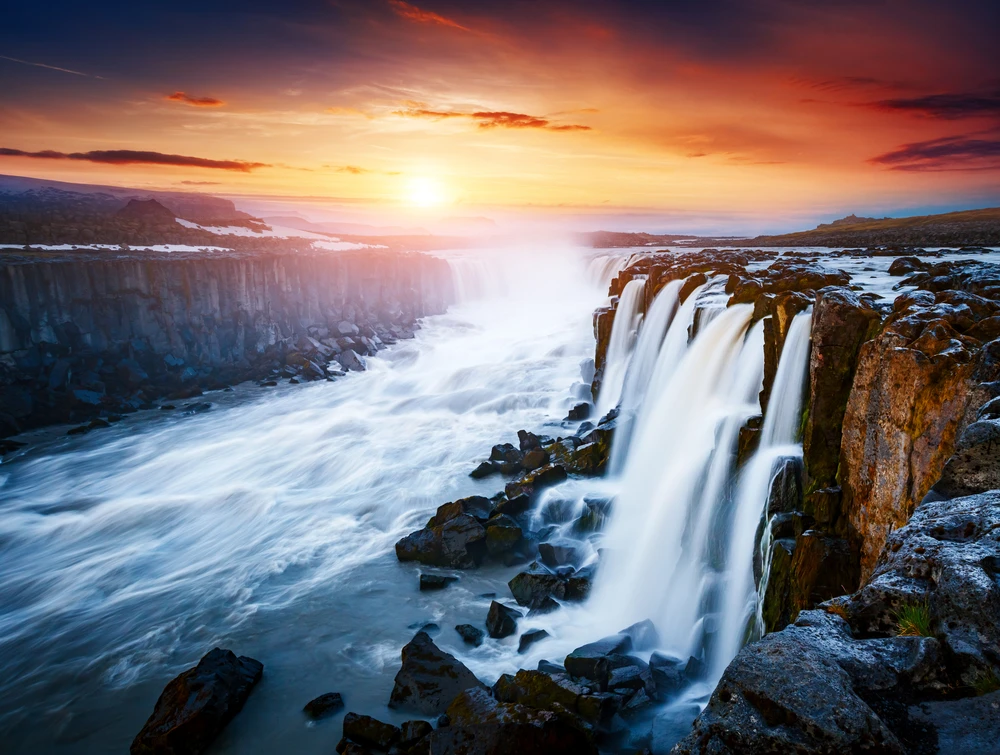
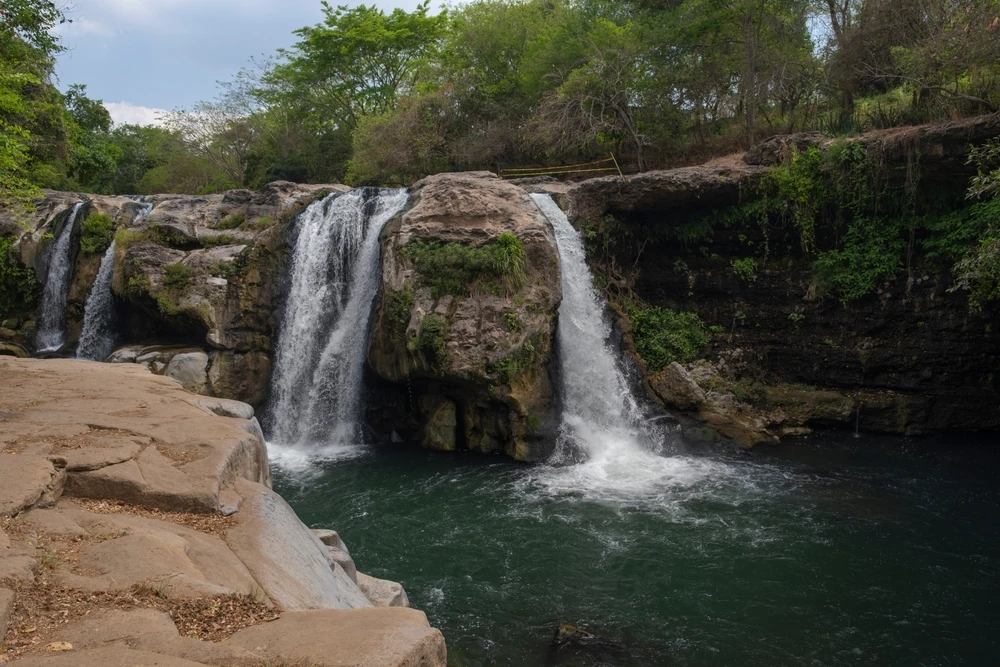
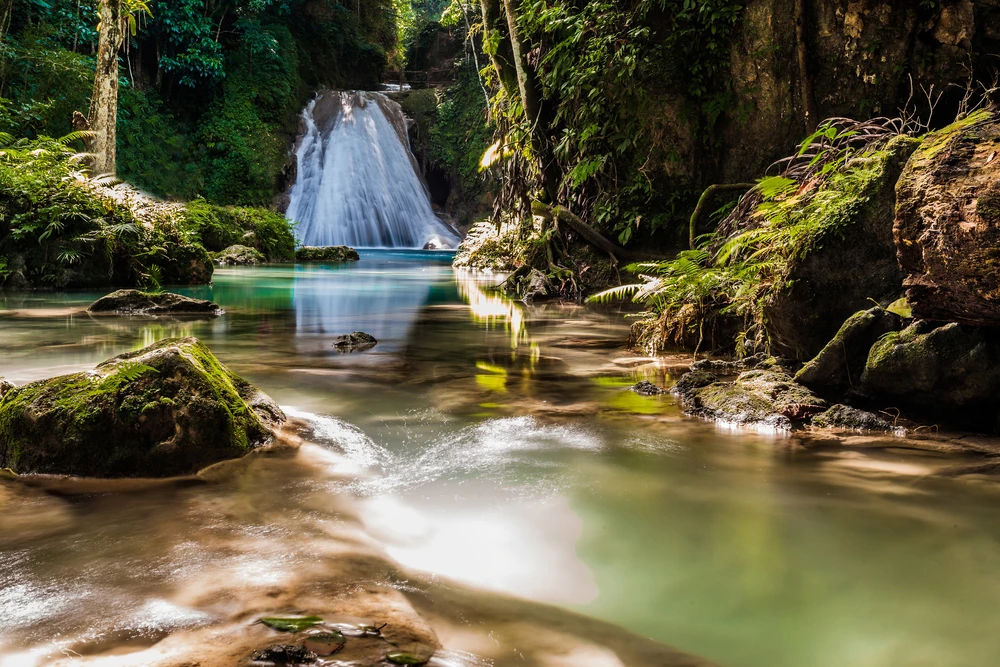
Shorsky National Park boasts several notable natural features that attract visitors. The “Saga Waterfall” is a multi-tiered cascade dropping 15 meters into a serene pool and grotto. The “Tsar’s Gate” is a prominent rock formation with a natural arch overlooking the Mrassu River.
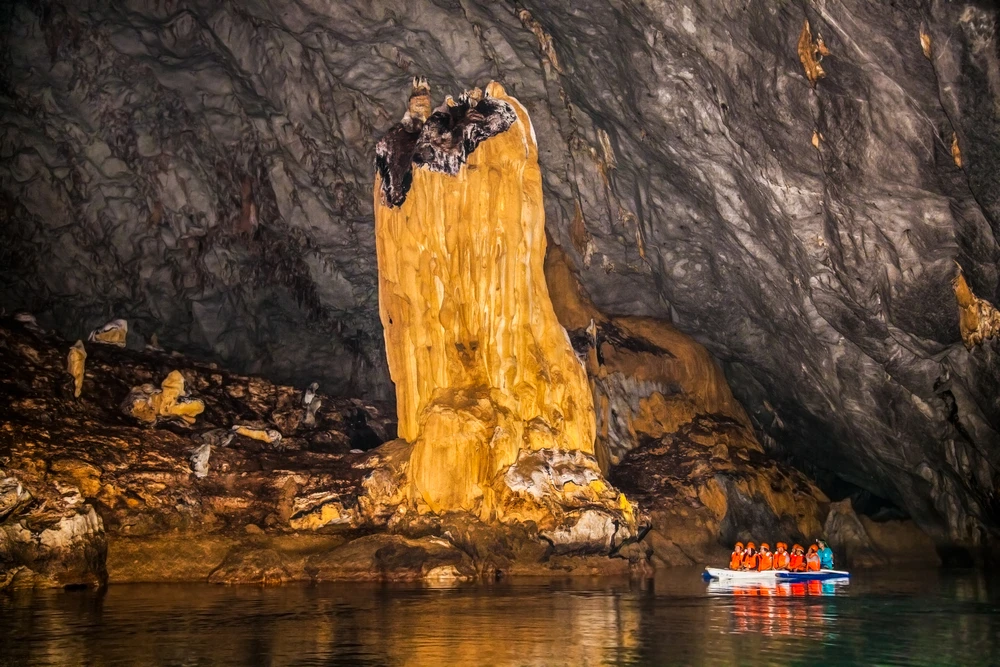
Caving enthusiasts can explore the “Moonlight” cave, extending 200 meters and adorned with stalactites and stalagmites, and the “Azasskoy” cave, known for its expansive gallery. In total, the park contains over 60 documented caves and distinctive rock outcrops.
Visitors can engage with the park through various activities. Hiking and horseback riding trails traverse the diverse landscapes, offering immersive experiences in the dense forests and mountainous terrains. The Mrassu River provides opportunities for rafting, allowing visitors to navigate its scenic course.
For accommodations, the park maintains three shelters equipped with wooden huts suitable for year-round stays. To access the protected areas, visitors must obtain permits from the park headquarters in the town of Tashtagol.
Conservation efforts in Shorsky National Park have led to significant successes. The cessation of logging activities following the park’s establishment has allowed mature forests to regenerate, enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health.
The park’s management focuses on preserving the natural environment while promoting sustainable tourism practices. However, challenges persist, including mitigating human-wildlife conflicts and ensuring that increasing tourism does not negatively impact the park’s ecosystems.
Ongoing efforts aim to balance conservation objectives with the cultural and economic needs of the local communities, particularly the indigenous Shor people.